Introduction
(Article introduction authored by INCA Editorial Team)
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection, remains a major global health challenge. Its high heterogeneity complicates treatment, necessitating personalized approaches.
Recent research highlights phenotyping as a key strategy to classify sepsis subgroups based on clinical, biomarker, and genetic data. Advanced AI and big data methods now enable precise patient stratification, improving therapy effectiveness.
While challenges like standardization and clinical integration persist, phenotype-driven treatments hold great promise for enhancing patient outcomes and transforming sepsis management.
This review examines current advancements in sepsis phenotyping (Figure 1), highlighting the potential of these methods to tackle sepsis heterogeneity and optimize treatment protocols.
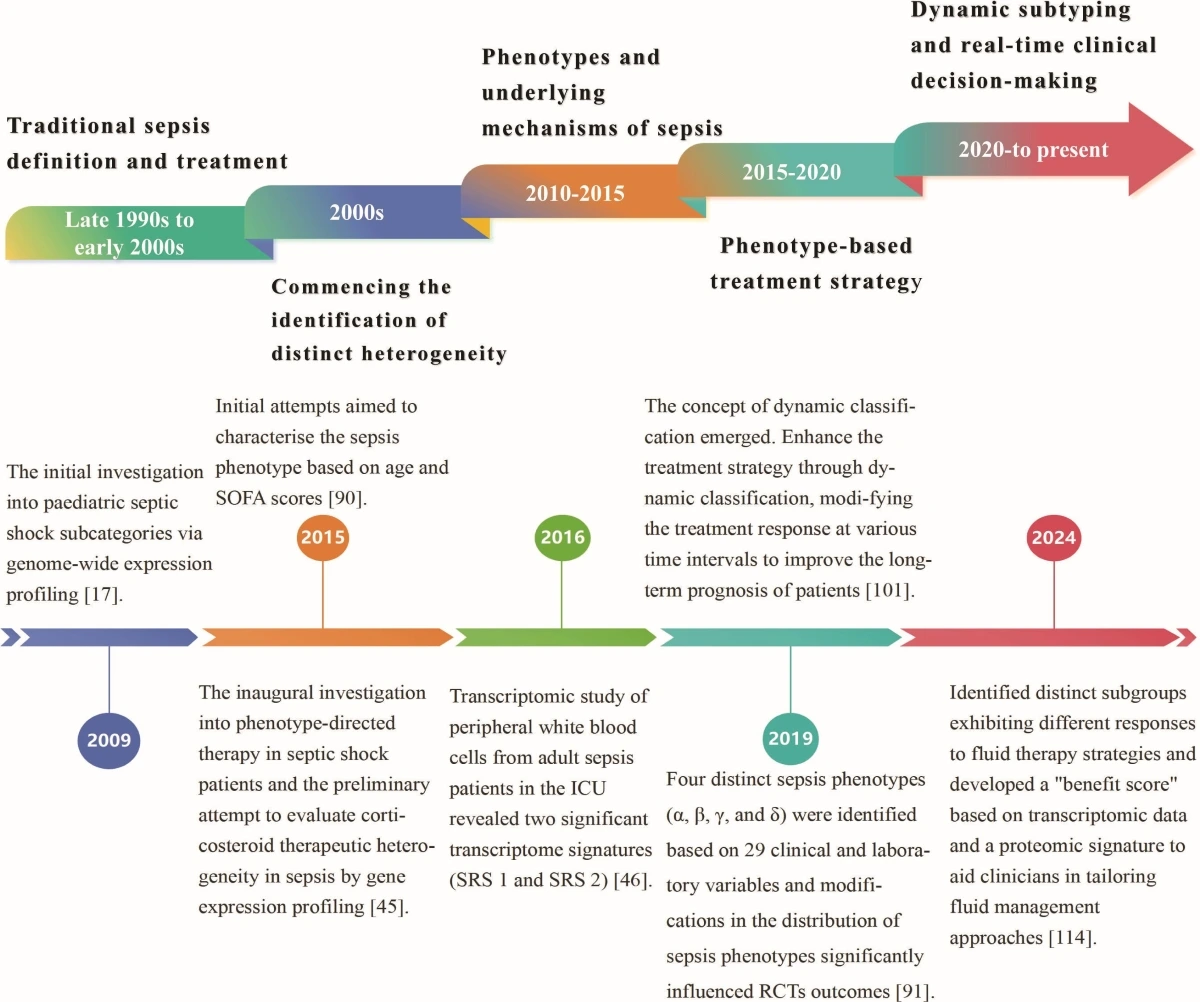
Figure 1. Chronology of the developmental history of sepsis classification.
The necessity of sepsis classification
Sepsis, a complex clinical disease, involves various immunological responses and patient characteristics. Current treatments, like hormone therapy and antibiotics, have shown limited efficacy due to the heterogeneous nature of sepsis.
Research suggests that stratifying patients by phenotype could lead to more effective treatments, as seen in patients with macrophage activation syndrome benefitting from targeted therapies.
Genomic studies have identified sepsis subphenotypes, paving the way for precision therapies. Understanding sepsis heterogeneity through advanced technologies could improve treatment outcomes.
Additionally, studies on sepsis recovery highlight the need for personalized post-ICU care. Integrating diverse omics data with AI technologies is crucial for developing precise sepsis therapies.
Bridging sepsis subphenotypes to treatment strategies
Sepsis heterogeneity challenges treatment efficacy, necessitating subphenotype classification to improve outcomes. Multiomics technologies like epigenomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics aid in molecular subtyping, biomarker identification, and treatment personalization.
Epigenomic changes impact immune responses, while transcriptomics reveal gene expression patterns linked to sepsis variability. Proteomics unveils protein biomarkers for disease severity assessment.
Metabolomics enriches understanding by analyzing metabolic alterations. Cytomics, focused on immune cell diversity, complements this understanding. Machine learning categorizes sepsis subphenotypes for tailored therapies. Specific subphenotypes exhibit varied responses to medications like corticosteroids and fluid resuscitation, emphasizing personalized treatment strategies guided by molecular profiles to optimize sepsis management.
Advancing phenotype-guided therapies
The research paper emphasizes the need for phenotype-guided therapies in sepsis management. Investigations into sepsis subphenotypes have revealed the disease’s heterogeneity and the potential for tailored treatment strategies.
However, further validation and enhancement are required to convert these insights into effective therapies. Standardized validation across diverse populations and clinical settings is crucial, as current research is limited by retrospective or cohort data.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that subphenotypes are associated with varying treatment responses, highlighting the importance of pre-screening to optimize therapy and improve prognosis.
The paper also discusses the challenges of sepsis phenotyping, including data heterogeneity and the integration of emerging techniques like machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Advantages
Revealing biological mechanisms and therapeutic targets, multi-omics technologies offer precise stratification and personalized treatment in sepsis research.
However, challenges like cost and technical complexity hinder accessibility, especially in resource-limited settings.
Interdisciplinary collaboration is key to integrating clinical, biological, and computational expertise for improved methodologies.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence enhance treatment response diversity identification but face adoption obstacles like transparency and scalability issues. Economical, interpretable AI models and robust ethical frameworks are crucial for practical implementation and data governance.
Overcoming these barriers can advance sepsis phenotyping, leading to tailored therapies and improved patient outcomes.
Expanding the scope of phenotypic research
A holistic understanding of sepsis demands multi-organ system assessments beyond blood-based approaches. Omics technologies offer molecular insights, yet bridging the gap to clinical utility requires comprehensive phenotypic evaluations.
Sepsis affects various organs differently, emphasizing the need for cross-tissue exploration of gene expression, protein function, and metabolite regulation, especially in lungs, liver, and kidneys.
Integrating multi-omics with cross-organ studies will refine sepsis comprehension for targeted organ-specific therapies. Longitudinal sampling is crucial to understand transients from stable phenotypic traits, improving subtype classification and personalized treatments.
Dynamic studies tracking phenotypic changes enable tailored interventions, proving essential for precision medicine progress.
Conclusions
The review highlights the importance of understanding the heterogeneity of sepsis to develop personalized therapeutic strategies and improve patient outcomes.
It synthesizes advances in clustering algorithms, multi-omics technologies, and artificial intelligence, providing a framework for identifying distinct sepsis subtypes with varied treatment responses. These insights pave the way for discovering novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets, underscoring the transformative potential of precision medicine.
However, challenges such as phenotyping standardization, dynamic data integration, and clinical translation must be addressed through interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative research.
By bridging these gaps, future efforts can fully implement phenotype-driven therapies, transforming sepsis management, enhancing survival rates, and establishing a new paradigm for precision medicine in complex diseases.
Source: Zhang, Xue, et al. “Sepsis subphenotypes: bridging the gaps in sepsis treatment strategies.” Frontiers in Immunology 16 (2025): 1546474.